
Each production consists of a non-terminal called the left side of the production, an arrow, and a sequence of tokens and/or on- terminals, called the right side of the production. The productions of a grammar specify the manner in which the terminals and non-terminals can be combined to form strings. Terminals are the basic symbols from which strings are formed.Ī set of productions (P). The non-terminals define sets of strings that help define the language generated by the grammar.Ī set of tokens, known as terminal symbols (Σ). Non-terminals are syntactic variables that denote sets of strings. In this section, we will first see the definition of context-free grammar and introduce terminologies used in parsing technology.Ī context-free grammar has four components:Ī set of non-terminals (V). CFG is a helpful tool in describing the syntax of programming languages.

It implies that every Regular Grammar is also context-free, but there exists some problems, which are beyond the scope of Regular Grammar. Therefore, this phase uses context-free grammar (CFG), which is recognized by push-down automata.ĬFG, on the other hand, is a superset of Regular Grammar, as depicted below: Regular expressions cannot check balancing tokens, such as parenthesis.
But a lexical analyzer cannot check the syntax of a given sentence due to the limitations of the regular expressions. We have seen that a lexical analyzer can identify tokens with the help of regular expressions and pattern rules.

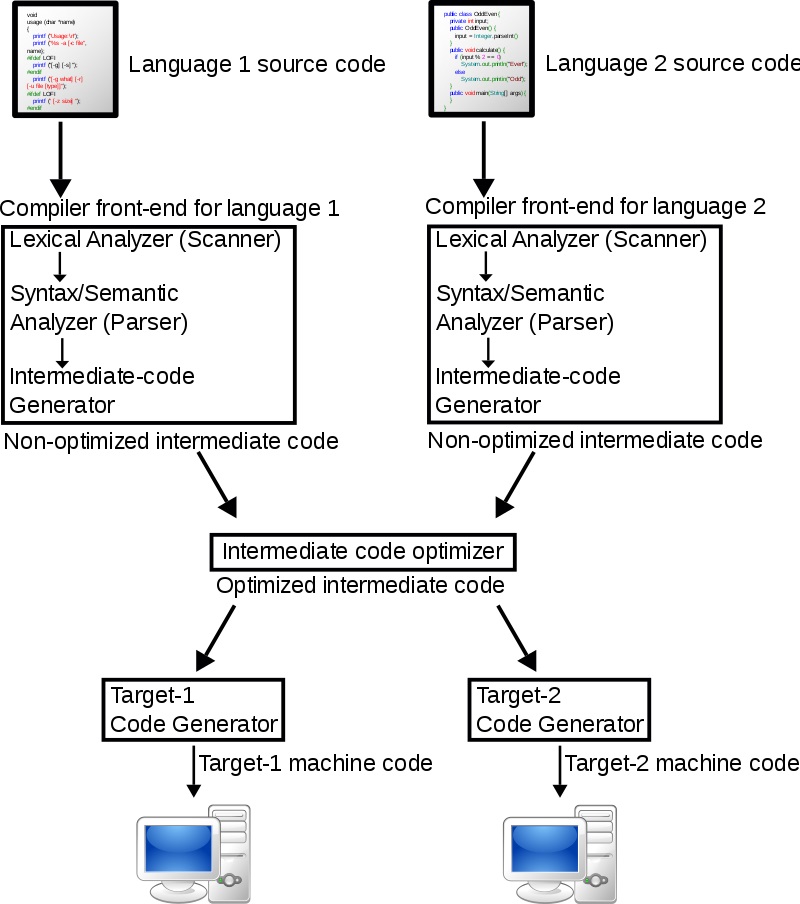
In this chapter, we shall learn the basic concepts used in the construction of a parser. Syntax analysis or parsing is the second phase of a compiler.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
